Blue Light Protection: Understanding the Risks and Solutions
What Is Blue Light? Understanding Its Wavelength Range and Sources from Digital Devices
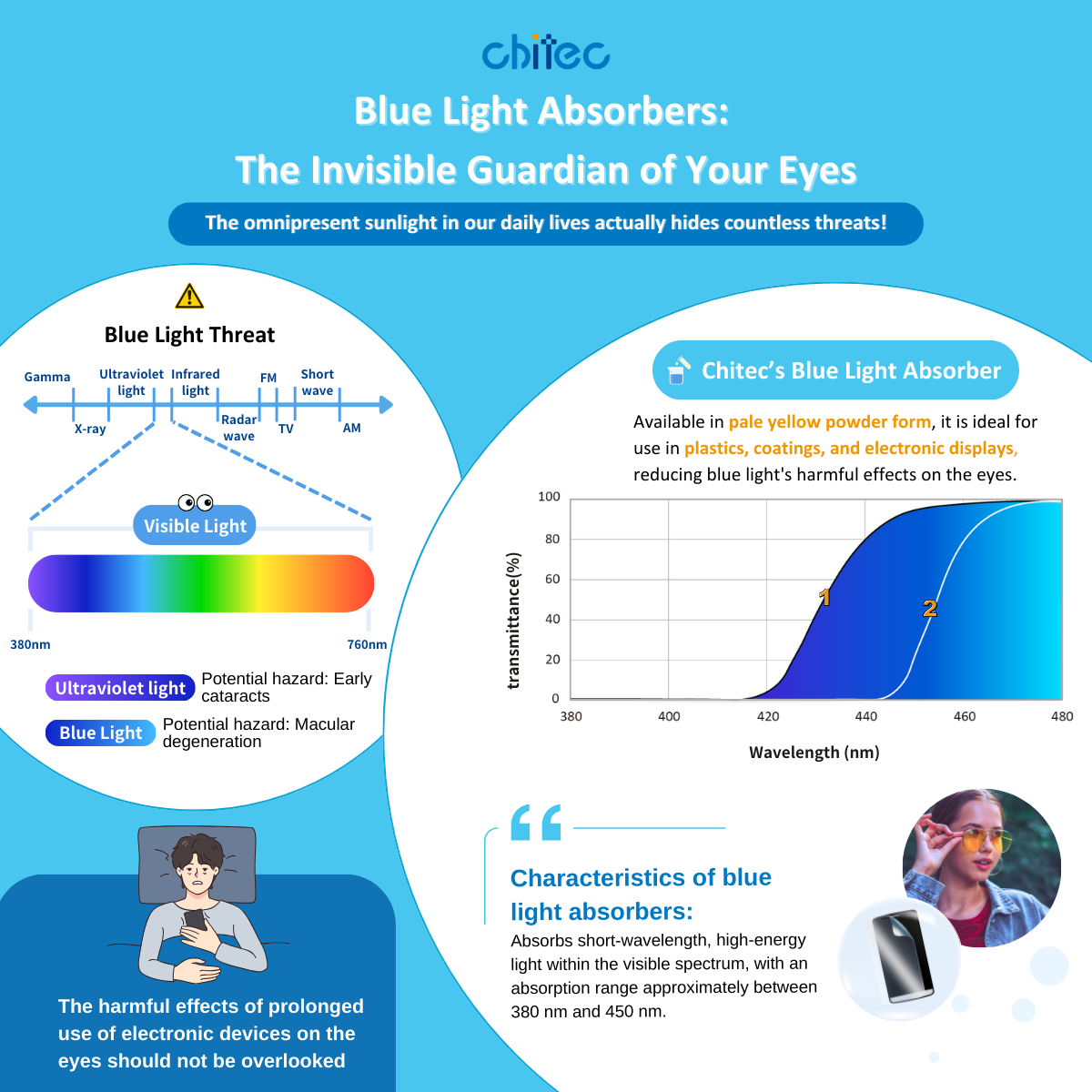
In our daily lives, sunlight is omnipresent, but it carries hidden risks. The solar spectrum is divided into three main parts: ultraviolet, visible light, and infrared. Visible light, which our eyes can detect, ranges from 380 to 780 nm and is split into seven colors: red, orange, yellow, green, blue, indigo, and violet. With the widespread use of LED technology, exposure to blue light has increased significantly. Devices such as televisions, computers, laptops, mobile phones, and tablets all emit substantial amounts of blue light.
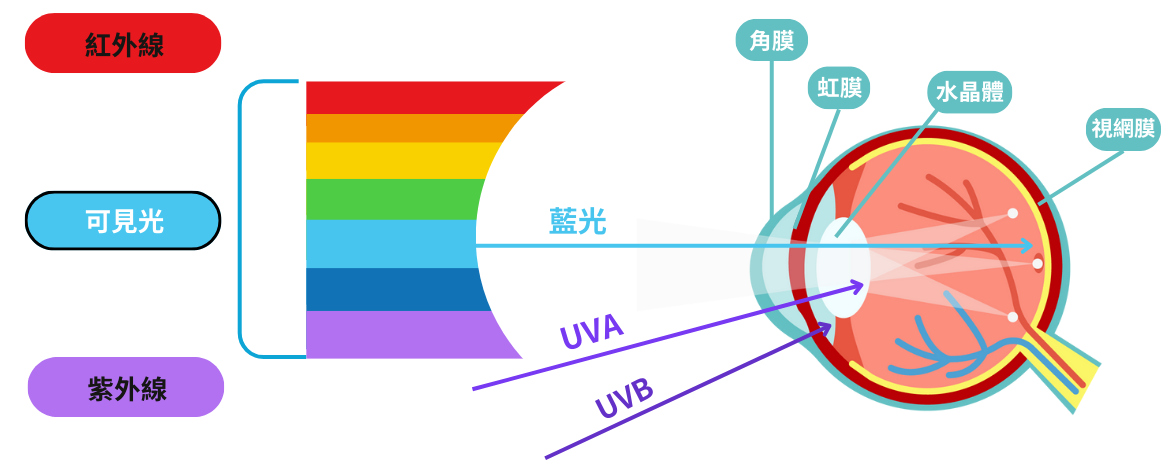
Unlike ultraviolet light, which is usually blocked by the cornea and lens and thus rarely reaches the retina, blue light behaves differently. Blue light is defined as visible light with wavelengths between 380 and 500 nm, and it is sometimes further divided into blue-violet light (approximately 380 to 450 nm) and blue-green light (approximately 450 to 500 nm). This type of light has shorter wavelengths and higher energy, making it capable of penetrating the cornea and lens, reaching the retina, and potentially harming eye health.
How Blue Light Affects Eye Health: Risks to the Retina, Sleep, and Aging
How Viewing Distance and Exposure Time Affect Blue Light Risks
The impact of blue light on the eyes depends primarily on the duration and frequency of exposure. Prolonged exposure, especially during evening hours, can affect sleep quality and overall health. While the blue light intensity from electronic devices is generally low, continuous long-term use can gradually increase the strain on the eyes.
Frequent exposure to bright screens at night may lead to eye fatigue, blurred vision, and disrupted sleep patterns, as blue light can suppress melatonin production and delay sleep onset. Reducing screen brightness or using night mode can help mitigate these effects.
Proximity to blue light sources is also a key factor in determining risk. The closer you are to a light-emitting device, the higher the intensity of light that reaches your eyes. Devices like phones, tablets, and computers are often used at a distance of only 30 to 50 centimeters from the eyes. Even though the blue light intensity may not be extremely high, prolonged use at such close distances can cause eye fatigue, dryness, and even impact vision.
Keeping a reasonable distance from these screens helps to reduce blue light exposure, as light intensity diminishes with distance. For larger screens like televisions, maintaining a proper viewing distance can further minimize the effects of blue light on the eyes.
Blue Light–Induced Oxidative Stress and Cellular Damage: Mechanisms Behind Cataracts and Macular Degeneration
When the lens and retina absorb blue light, oxidative reactions may occur, generating free radicals. Accumulation of these free radicals can lead to cellular damage, potentially resulting in conditions like cataracts or macular degeneration. Such damage may cause distortions in the field of vision or impair color perception. For aging eyes, blue light's harmful effects are even more pronounced, exacerbating vision problems over time.
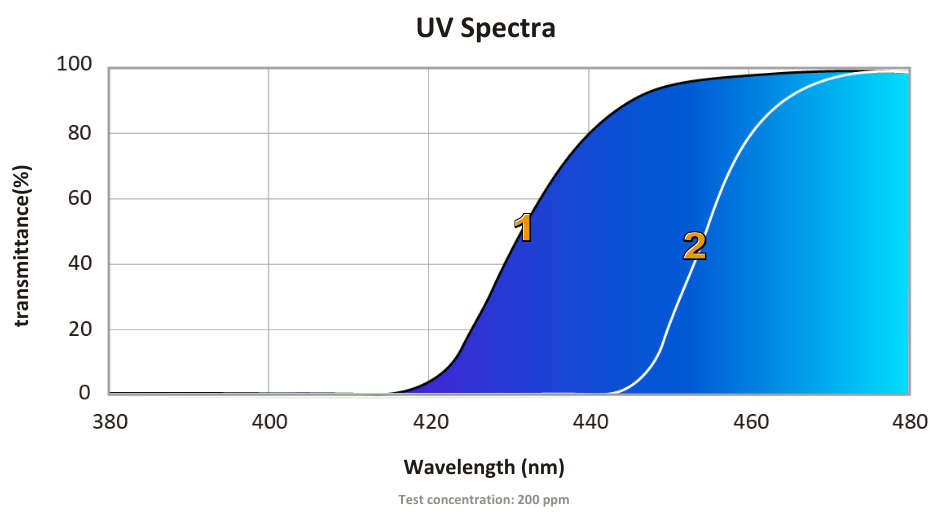
With the rapid advancement of technology, the time spent using digital devices has increased significantly. Many people spend more than eight hours a day staring at screens, making the cumulative effects of blue light more noticeable. Medical research shows that short-wavelength blue light around 420 nm can affect retinal neurons, with exposure to 411 nm (at 4.5W/m²) potentially causing retinal neuron cell death within 24 hours. Conversely, blue light around 470 nm shows almost no impact. Therefore, filtering light between 400 and 420 nm is crucial for preventing eye diseases. Our advanced blue light absorber is designed to tackle this issue, offering powerful protection by absorbing high-energy blue light in the range of 380 to 450 nm. Available in pale yellow powder form, it is ideal for use in plastics, coatings, and electronic displays, reducing blue light's harmful effects on the eyes.

Introduction to Blue Light Absorber Technology: High-Energy Blue Light Filtering and Optical Conversion
Our blue light absorber is built with a meticulously engineered molecular structure that features chromophore with conjugated double bonds and aromatic ring systems. This design enables strong light absorption and energy conversion.
When blue light enters a material, the absorber's chromophore converts high-energy blue light photons into low-energy heat, significantly reducing potential damage to eye tissues. Additionally, the absorber uses a precise optical filtering mechanism that selectively absorbs high-energy blue light in the 380 to 450 nm range. This filtering effect acts as an invisible barrier, blocking harmful blue light from penetrating the cornea and lens, preventing it from reaching the retina. By doing so, it dramatically reduces blue light-induced photo-oxidative damage, effectively protecting the eye's cells.
Applications and Market Trends of Blue Light Absorbers in Plastics, Coatings, and Consumer Electronics
Blue light absorbers have quickly become a focal point for industries involved in electronic displays and lens manufacturing. As the global reliance on electronic devices continues to grow, the importance of blue light absorption technology will only increase. By 2034, the market for blue light absorbers is expected to see a compound annual growth rate of 8.6%, with applications expanding across various sectors. We are committed to developing and launching a series of advanced blue light absorbers that will be widely applied in plastics, coatings, and digital displays, providing businesses with comprehensive blue light protection solutions while enhancing eye health for end consumers. Looking ahead, we will continue to bring innovative technology to the market, ensuring that the convenience of modern technology and vision protection go hand in hand.
Want to Choose the Right Blue Light Absorber? Here's Our Recommendation:
Explore Our Products and Application InsightsOr Contact Us for Full Technical Data and Expert Support
Get in Touch


