Outdoor sunlight and intense UV exposure are the silent enemies of plastics, coatings, and films. Over time, they lead to yellowing, gloss loss, embrittlement, and cracking.
Just as our skin relies on sunscreen for protection, materials also need their own defense strategy.
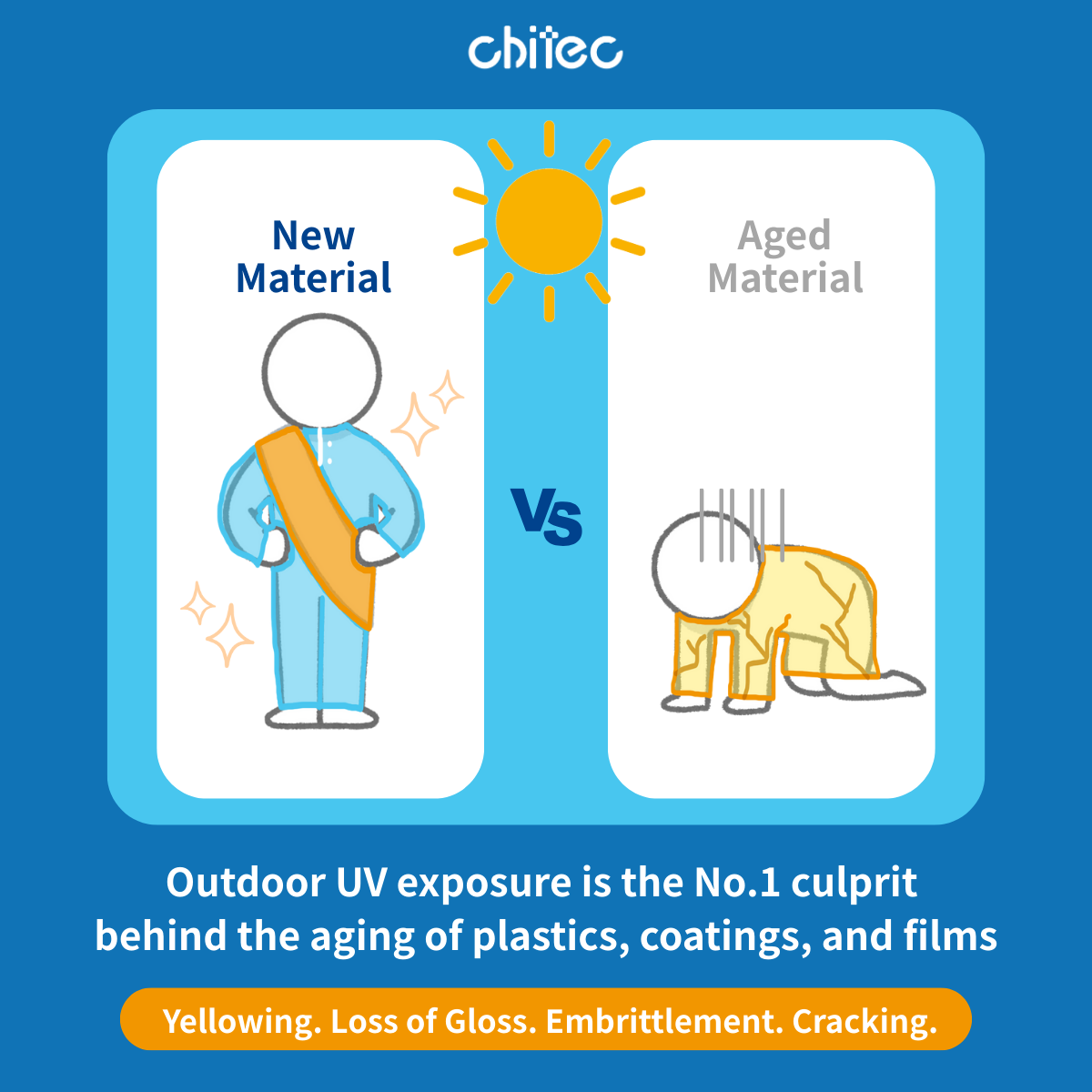
UV absorbers act as an invisible shield — intercepting and converting harmful UV radiation into harmless energy before it can damage the material. By allowing only visible light to pass through, they help preserve both appearance and structural integrity.
At the molecular level, UV absorbers are built with conjugated systems of double bonds (C=C) or aromatic rings. Their π electrons are highly sensitive to UV photons. When exposed to light at just the right energy level, these molecules absorb the photons, entering a temporary "excited state."
In milliseconds, the absorbed energy is released as heat or low-energy light, returning the molecule to its stable ground state. This molecular energy buffer prevents UV damage, ensuring long-term durability even in high-UV or outdoor conditions.

Key Design Factors for High-Performance UV Absorbers
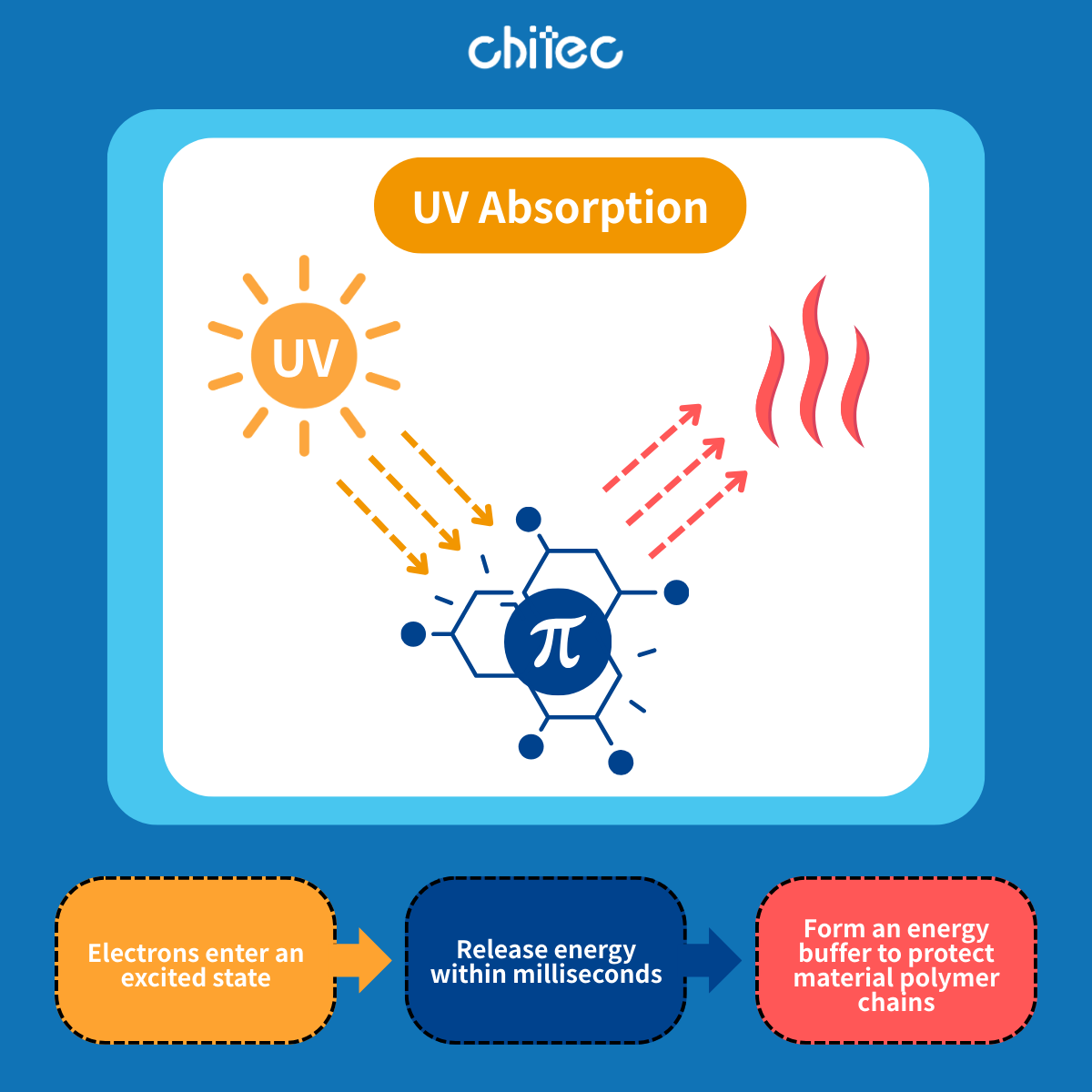
UV degradation is a cumulative process. Without precise design, gaps in absorption range or poor stability allow UV rays to penetrate, breaking polymer chains and accelerating aging.
Here’s what defines a high-performance UV absorber:
1. Accurate Absorption Range Matching
Different materials respond uniquely to UVA and UVB. Tailoring the absorption curve ensures optimal protection.
Transparent plastics like optical films, PC, and PMMA are especially prone to gloss loss and discoloration.
For outdoor or high-durability applications, combining UVB and UVA absorbers with HALS (Hindered Amine Light Stabilizers) delivers full-spectrum coverage from 280–400 nm.
2. Extended Conjugation: Shifting the Absorption Peak
Molecular conjugation (via extended double bonds and aromatic rings) effectively red-shifts absorption, expanding protection from UVB to UVA.
- Longer conjugation systems (more double bonds or aromatic rings) red-shift the absorption peak, expanding coverage to 340–380 nm and beyond.
- Low polarity ensures compatibility and stable dispersion in nonpolar polymers like PP and PE, preventing migration or phase separation.
3. High Photostability: Efficient Energy Release
Effective UV absorbers must release absorbed energy safely without breaking down.
-
Non-radiative decay mechanisms safely dissipate energy as heat or molecular vibration.
-
Stable aromatic backbones and protective side groups resist oxidation and photodegradation.
-
Synergistic formulations that combine UV absorbers, HALS, and antioxidants create a three-level defense: UV blocking, radical scavenging, and anti-oxidation.
4. Excellent Compatibility Without Side Effects
A good UV absorber should not compromise the final product’s appearance or properties.
-
Uniform dispersion in substrates such as PC, PMMA, PET, TPU, UV-curable resins, and acrylic coatings.
-
Maintains high transparency and minimal haze, critical for optical and protective applications.
Common UV Absorber Families
-
Benzophenones
-
Benzotriazoles
-
Triazines
👉 Explore our full UV absorber portfolio here → Chitec UV Absorber Product List
Applications

- Cosmetics: Sunscreens, sunblock sprays
- Automotive: Headlamp covers, bumper coatings
- Outdoor Plastics: Garden furniture, PE piping
- Optical & Electronics: Solar panel protective films, optical filters
- Food & Beverage Packaging: Minimizing UV-induced degradation of contents
Product Benefits
-
Extends material lifespan
-
Maintains appearance and transparency
-
Reduces maintenance and replacement costs
-
Enhances weather resistance and brand trust
Looking for the right UV protection solution?
Reach out for custom formulation advice and technical support:
📧 sales@chitec.com


建議您使用以下瀏覽器觀看本網站,
要下載瀏覽器,請直接點擊以下:以獲得最佳瀏覽效果。